What is Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
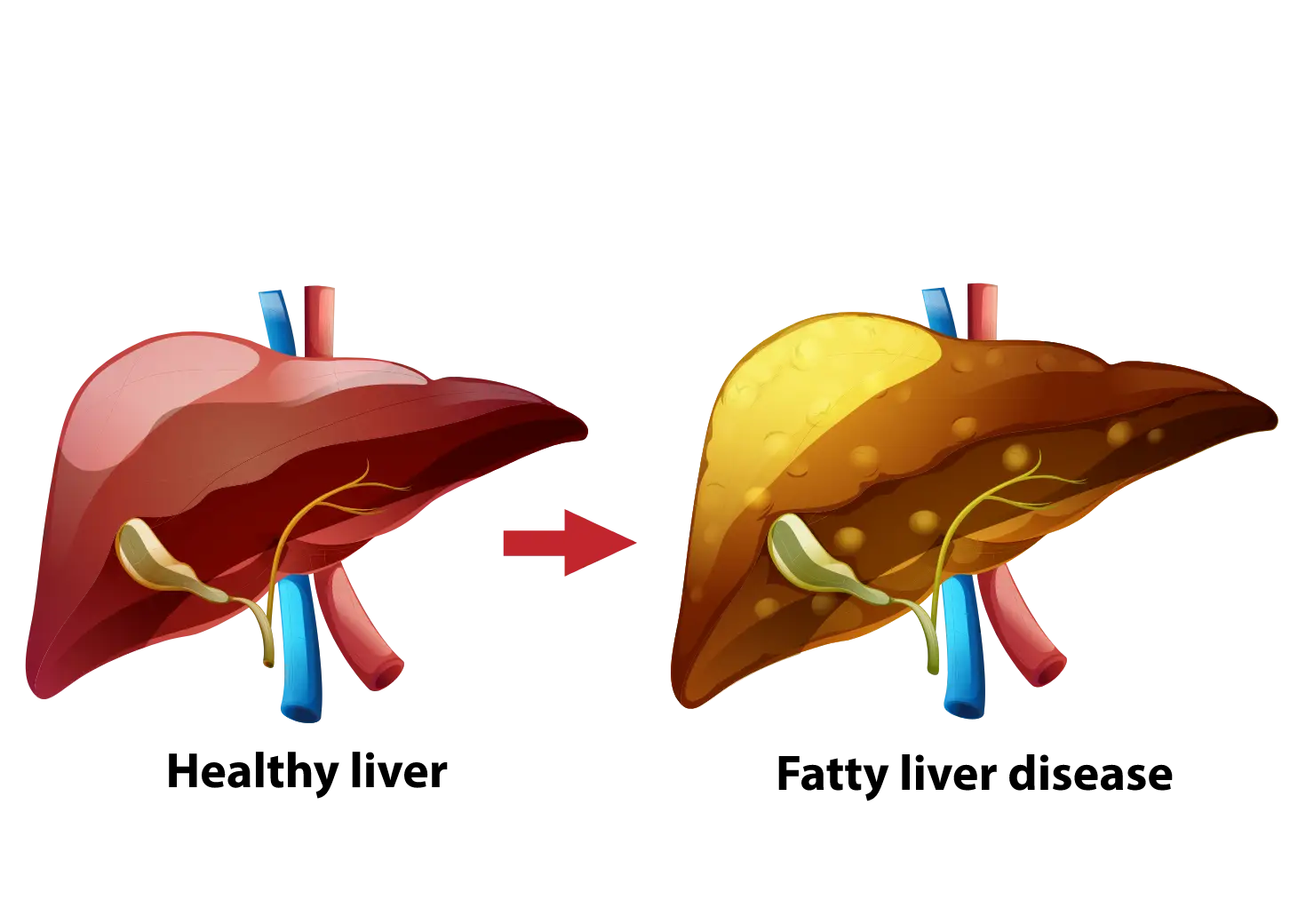
When the fat accumulates inside your liver cells causing damage to liver cells is called fatty liver disease. It may even lead to liver failure if not treated for a longer period of time. Initially, the disease is asymptomatic, with symptoms only showing when the liver has been damaged severely. Hence it may be called a silent killer.
Fatty liver is of two types i.e
- Alcoholic fatty liver
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Alcoholic fatty liver is due to excessive intake of alcohol. Nearly 90% of heavy drinkers develop fatty liver. In heavy drinkers, it is important to recognize the signs as early as possible because repeated damage can lead to cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is the irreparable damage caused to the liver by permanent scarring of the liver. A connection with other metabolic dysfunctions cannot be ruled out. Patients suffering from chronic alcoholism may need support from an alcohol deaddiction center to avoid liver failure due to alcohol intake.
One such deaddiction center is Tulasi Healthcare which helps people to give up alcohol drinking in chronic alcoholism cases. At Tulasi Healthcare rehabilitation of chronic alcoholics is possible. It is a full-fledged rehabilitation center with a 225-bed capacity, where de-addiction treatment for alcohol is given.
Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)is due to a heavy cholesterol diet or other metabolic disturbances. It has got close association with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Moderate or heavy alcohol use can cause additional damage and fat accumulation in the liver in people with NAFLD. Therefore patients with NAFLD should avoid alcohol entirely if possible.
Stages of Fatty Liver Disease
The fatty liver disease can be divided into three grades or stages depending on the amount of afat stored and the level of damage caused to liver.
GRADE 1 : in this stage patient is asymptomatic and disease is not diagnosed until routine check up or abdominal sonography is done for other indications. This stage is reversible because no irreversible damage to liver is caused by this time.
GRADE 2: in this stage mild symptoms are seen such as pain in upper right quadrant of abdomen or below the ribs, nausea and some inflammation in the liver cells. Inflammation is the sign that liver is self healing. Like the first stage this stage is reversible too , because no irreversible damage to liver is caused by this time. The condition is known as liver steatosis.
GRADE 3: In this stage damage becomes irreversible as scarring of liver tissue has already taken place and the condition is known as liver cirrhosis.
Risk Factors for Fatty Liver Disease
- Obesity
- Liver Injury
- Dyslipidemia
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hypertension
During the process of alcohol metabolism, alcohol, and its metabolites have various effects on metabolic-related abnormalities. Some examples are given below:
Obesity and alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption is associated with increased body weight as well as waist circumference due to increased total energy intake and impaired peripheral or central insulin signaling pathways.
Although light to moderate alcohol consumption is likely to maintain normal body weight through improved insulin resistance.
Liver injury and alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption exerts synergistic effects on liver injury. In obese patients, this effect is more prominently seen. Two important mechanisms are the Liver-adipose tissue axis and the liver-gut axis.
Lipid metabolism and alcohol consumption: Alcohol is related to increased triglyceride and HDL levels. However, the anti-oxidant effects of HDL are different showing impaired anti-oxidative properties in heavy alcohol consumption with poor liver function. However low to moderate alcohol consumption shows enhanced anti-oxidative properties.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus and alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus mainly because of impaired insulin signaling, decreased insulin secretion, and insulin resistance. However low to moderate alcohol consumption, especially in combination with a healthy lifestyle is related to improved insulin resistance and decreased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus partly through regulating the expression of adiponectin.
Hypertension and alcohol consumption: The effects of alcohol consumption on blood pressure are common. Heavy alcohol consumption is usually associated with significantly increased blood pressure and risk of hypertension, while in low to moderate alcohol consumption risk of hypertension is lower.
The treatment for alcoholic fatty liver disease is available at Tulasi Healthcare Center located at Sector- 64, Gurgaon. Here a team of Psychiatrists, M.B.B.S doctors, Psychologists, and Gastroenterologists (available on call) help you with alcohol addiction treatment as well as Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by bringing lifestyle changes and following a proper diet.

